Relative Humidity
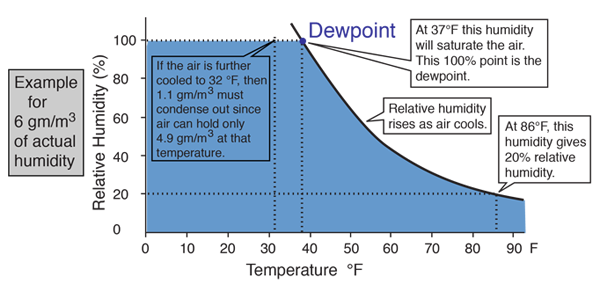
The amount of water vapor in the air at any given time is usually less than that required to saturate the air. The relative humidity is the percent of saturation humidity, generally calculated in relation to saturated vapor density.
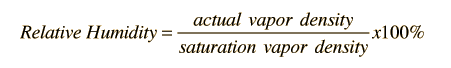
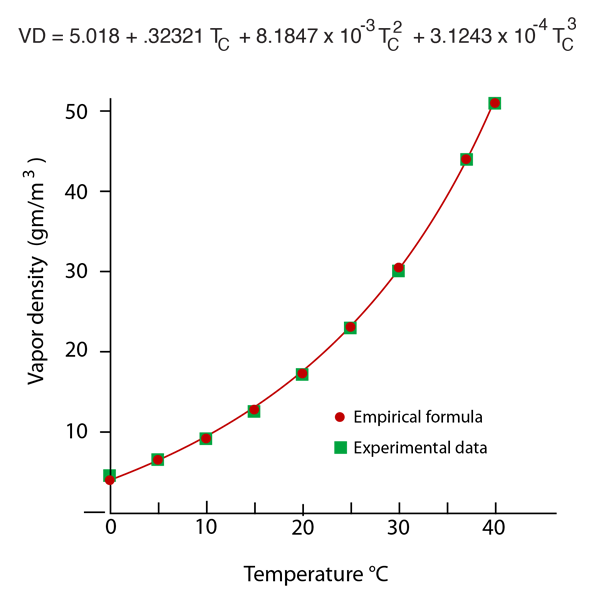
The most common units for vapor density are gm/m3. For example, if the actual vapor density is 10 g/m3 at 20°C compared to the saturation vapor density at that temperature of 17.3 g/m3 , then the relative humidity is
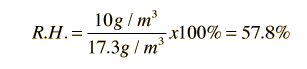 | Calculation |
The relative humidity can be equivalently defined in terms of the water vapor pressure in the air compared to its saturation vapor pressure.
|
| Saturation vapor pressure | Dewpoint | Relative humidity calculation |
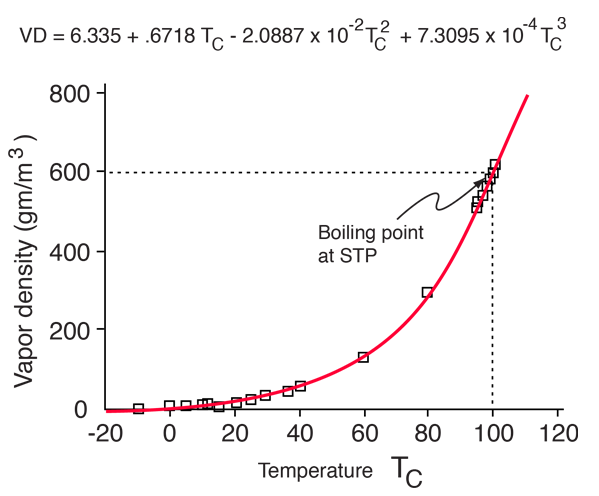
| Saturation vapor pressure and density for water |
Kinetic theory concepts
Applications of kinetic theory
Vapor application concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Thermodynamics | R Nave |