Lactate
Lactate is produced in the process of fermentation in cells. When there is not sufficient oxygen to support aerobic respiration in cells, the anaerobic respiration process produces lactate and ethanol. If the lactate cannot be used in the cell where it is produced, it may be transferred to the liver and be converted to glucose via gluconeogenesis as part of the Cori cycle. With sufficient oxygen, lactate may be oxidized back to pyruvate in muscle cells, heart cells, and brain cells. It may then be directly used in the TCA cycle. "During physical activity, up to 60% of the heart muscle's energy turnover rate derives from lactate oxidation."(wiki) | 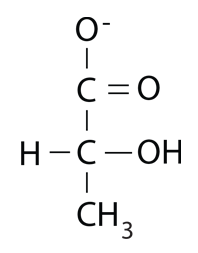 |
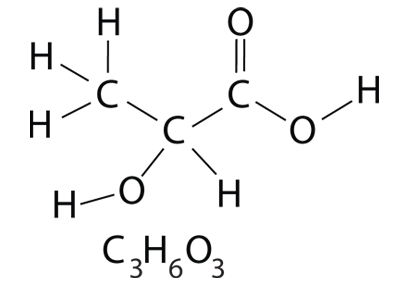 | Lactic acid. Lactate is the conjugate base of lactic acid. |
| Lactic acid Wiki |
Biochemical concepts
Chemistry concepts
References
Matthews, van Holde, & Ahern
Ch 16
| HyperPhysics*****Chemistry | R Nave |